A new battery developed by scientists can prevent fires and explosions if it overheats. The new design is a self-extinguishing rechargeable battery.
Battery Electrolyte
In a study published in Nature Sustainability, researchers replaced the highly combustible electrolyte with materials commonly found in fire extinguishers. An electrolyte found in batteries allows electricity to flow between battery terminals. Typically, the conventional electrolytes found in batteries comprise a lithium salt and an organic solvent. Both of these are flammable and can cause explosions if overheated.

However, the researchers did some work to replace the flammable electrolyte. They modified commercial coolants, which are used to suppress flames, to act as a battery electrolyte. By doing this, the commercial coolants were compatible with any battery chemistry. Furthermore, it was fireproof and heat-resistant, two things the conventional electrolyte isn’t capable of.
Explore Tomorrow's World from your inbox
Get the latest science, technology, and sustainability content delivered to your inbox.
I understand that by providing my email address, I agree to receive emails from Tomorrow's World Today. I understand that I may opt out of receiving such communications at any time.
The Test
To test the flame-resistant electrolyte, it had to go through a series of conditions. Researchers put it through a wide range of temperatures. They found that it worked when under extremely cold temperatures…minus 100-175 degrees Fahrenheit, to be exact. Not only that, but their tests also showed the electrolyte transferred heat away from the battery, effectively extinguishing any internal fires.
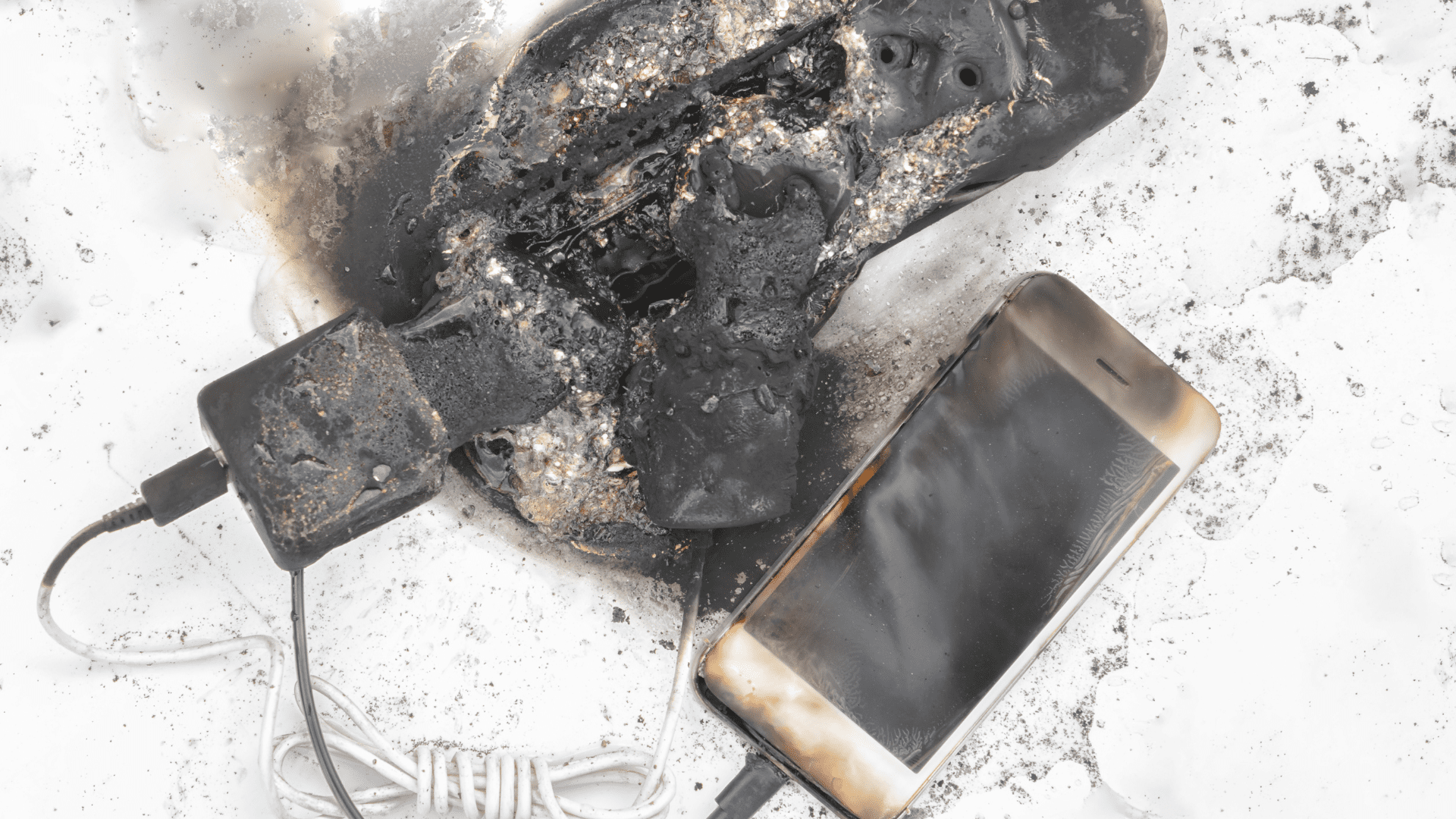

When batteries are punctured it creates an internal short circuit, which is also a risk for a fire. To test the new electrolyte’s ability to withstand being punctured, researchers also performed a nail penetration test. It’s a common method to test battery safety. Once they hammered a nail into the battery, they saw no signs of flames. Moreover, it was able to withstand the impact.
Pros and Cons
One advantage of the new design is that it has the potential to make lithium-ion batteries safer. Also, it allows more time for longer-term improvements that also prevent fires or overheating. Lithium-ion batteries are used in a lot of electronics and even electric vehicles but pose a safety risk. High outdoor temperatures can also compromise a battery’s safety and durability. Another safety issue in lithium-ion batteries is if they are charged too quickly they develop dendrites which are sharp lithium needles that can puncture the battery. Puncturing a battery causes a short circuit and risks a fire.
There are, however, some challenges with their alternative electrolyte. For example, common fire-resistant materials contain expensive fluorine and phosphorus, which can harm the environment. Researchers say they will continue to search for more sustainable and cost-effective alternatives.