Though robots have become sophisticated at accomplishing tasks like assembling parts, lifting boxes, and handling hazardous materials, their role in creative fields has been minimally studied. Enter Robot Drummer: the humanoid robot that can play complex drum patterns with technical and expressive skills comparable to humans.
This Robot Doesn’t Miss a Beat
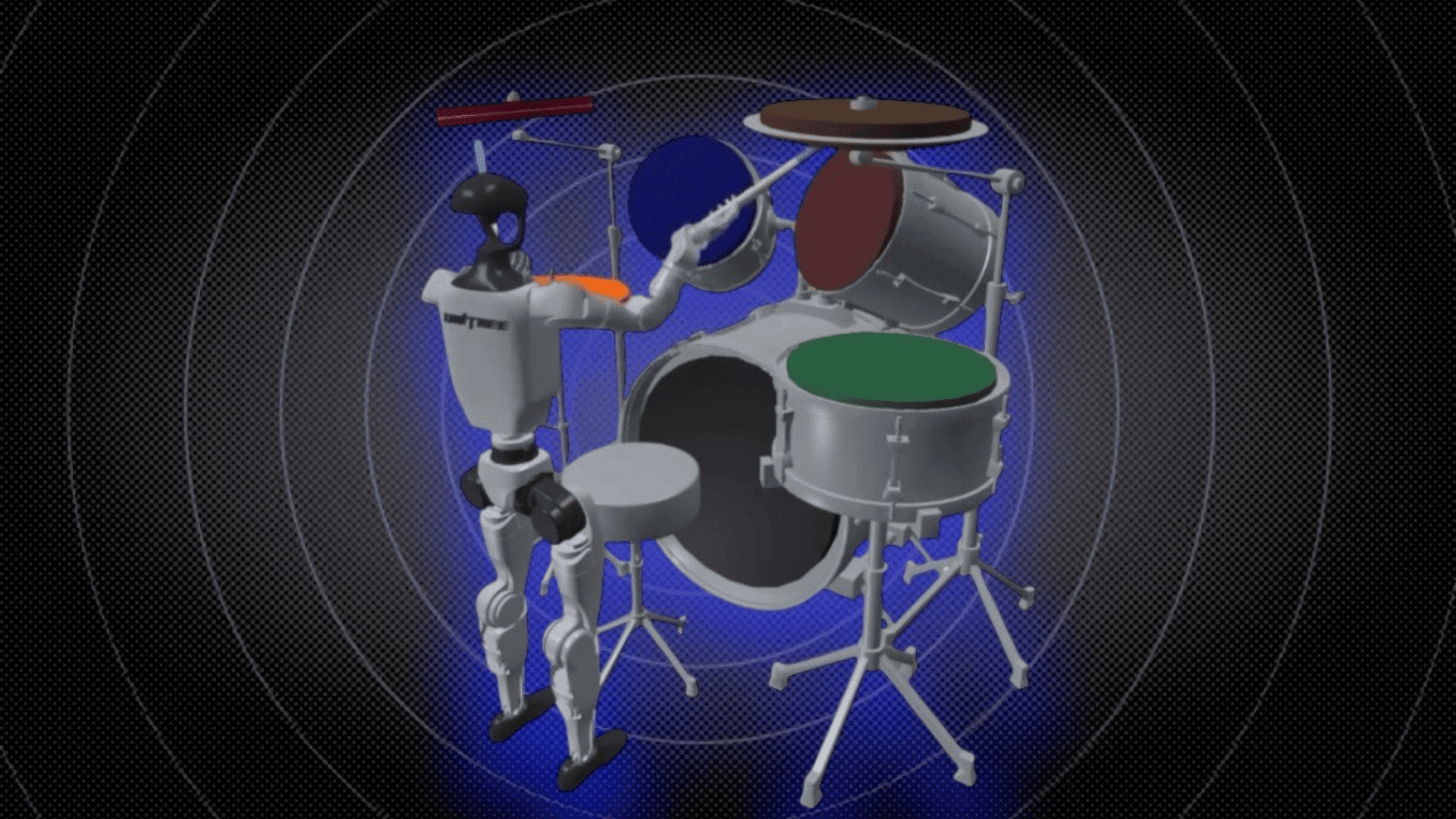

According to researchers at SUPSI, IDSIA, and Politecnico di Milano, who were behind the creation of Robot Drummer, the design was a spontaneous decision.
“The idea for Robot Drummer actually emerged from a spontaneous conversation over coffee with my co-author, Loris Roveda,” first author Asad Ali Shahid told Tech Xplore.
Shahid also stated that drumming was a good test for a humanoid robot in a creative field because it requires physicality, rhythm, and quick coordination. After constructing a machine learning system that allowed the robot to play entire tracks on a drum kit, they tested the simulation on the G1 humanoid robot from Unitree.
According to Interesting Engineering, the music was translated into a “rhythmic contact chain” or a precisely timed sequence of drum strikes. Each piece of music was represented by a chain of precisely timed cues telling the robot which drums to strike and when.
After the robot practiced to hone its skills, it began displaying human-like behaviors, such as cross-arm hits and stick switching. Robot Drummer was tested with a series of genres, including songs like “In the End” by Linkin Park and “Living on a Prayer” by Bon Jovi.
Researchers reported that the robot achieved precision of over 90% on many tracks, noting that it also learned to plan for upcoming drum strikes. The team behind the project is planning to move the technology from simulation to hardware while expanding its abilities to adapt to music cues in real time.
This type of technology could one day allow robotic performers to appear alongside live bands on stage. The study appears in a recent arXiv preprint.