Neuralink engineers announced a major development from the company’s Blindsight device, which is supposed to restore vision in individuals with complete blindness. The company revealed promising results in the latest tests on a monkey. Blindight reportedly allowed a monkey to perceive visual cues that were not there.
Neuralink Blindsight
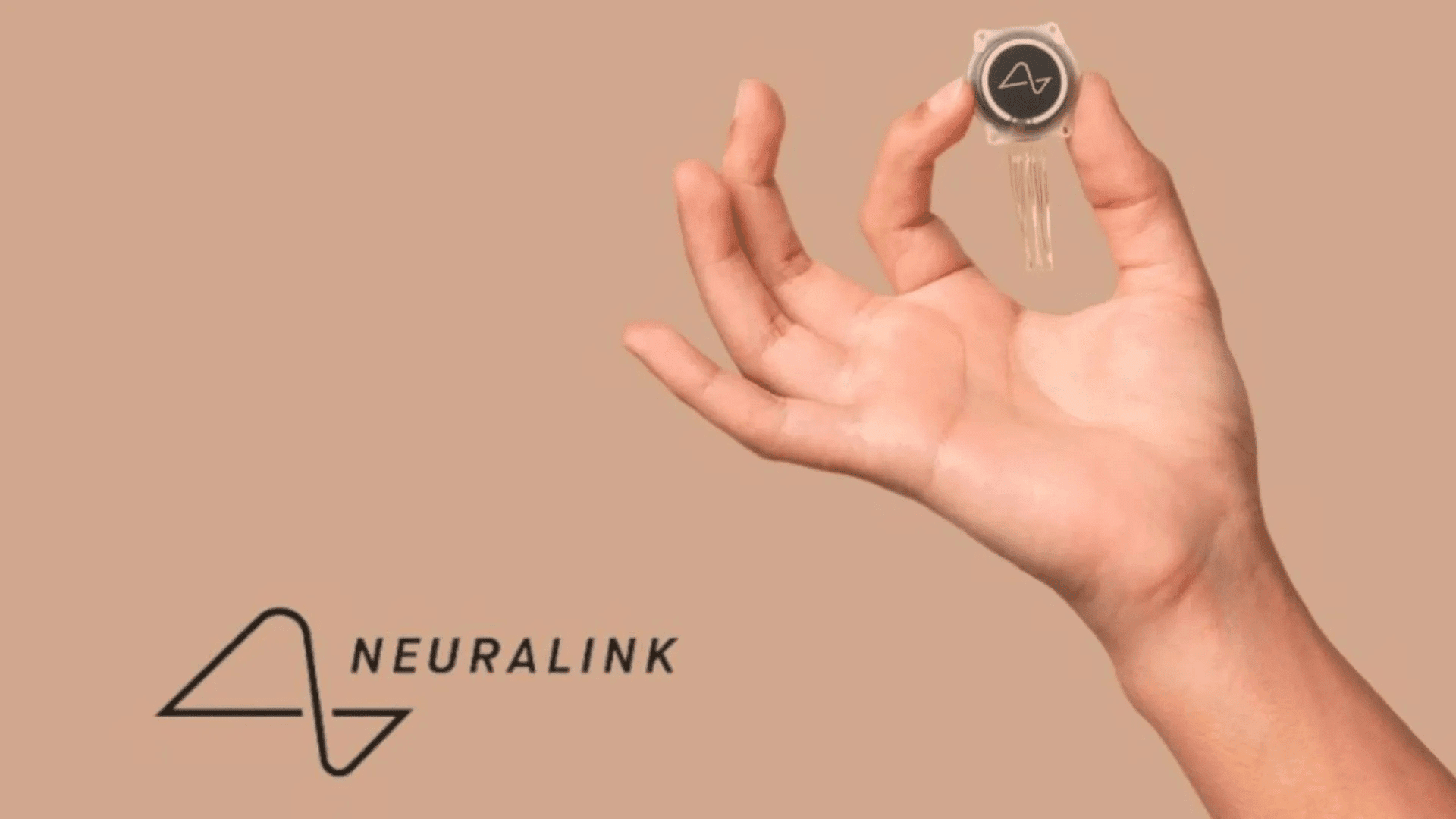

Blindsight is an experimental brain-computer interface (BCI) device. It is designed to bypass the eyes and optic nerve to create artificial vision by stimulating brain neurons.
According to Bloomberg, a chip was implanted into a monkey’s brain, responding two-thirds of the time to visual stimuli that researchers had artificially induced the monkey’s brain to perceive. This achievement marked a first for Neuralink.
Musk has said before that Blindsight’s short-term goal is to restore vision. However, his long-term goal is facilitating “superhuman” vision, including infrared or enhanced depth perception. The company has tested the technology on monkeys for years, but this is the first time that Neuralink has publicly discussed the results. Neuralink engineer Joseph O’Doherty shared the results at the Neural Interfaces Conference.
Despite testing on monkeys, the FDA has yet to approve testing the Blindsight device on humans. Musk said in March that Neuralink plans to test Blindsight on humans later this year.
During O’Doherty’s presentation at the conference, he said the company wants to incorporate a pair of glasses with Blindsight to help make the chip work. He also said that testing on monkeys has advantages. For example, the visual cortex in a monkey is closer to the brain than that of a human, making it easier to access.
Neuralink plans to use its surgical robots to reach deeper brain regions for human implantations.
In September of last year, Musk posted the company’s expectations on X and said, “To set expectations correctly, the vision will be at first be low resolution, like Atari graphics, but eventually it has the potential be better than natural vision and enable you to see in infrared, ultraviolet or even radar wavelengths, like Geordi La Forge.”