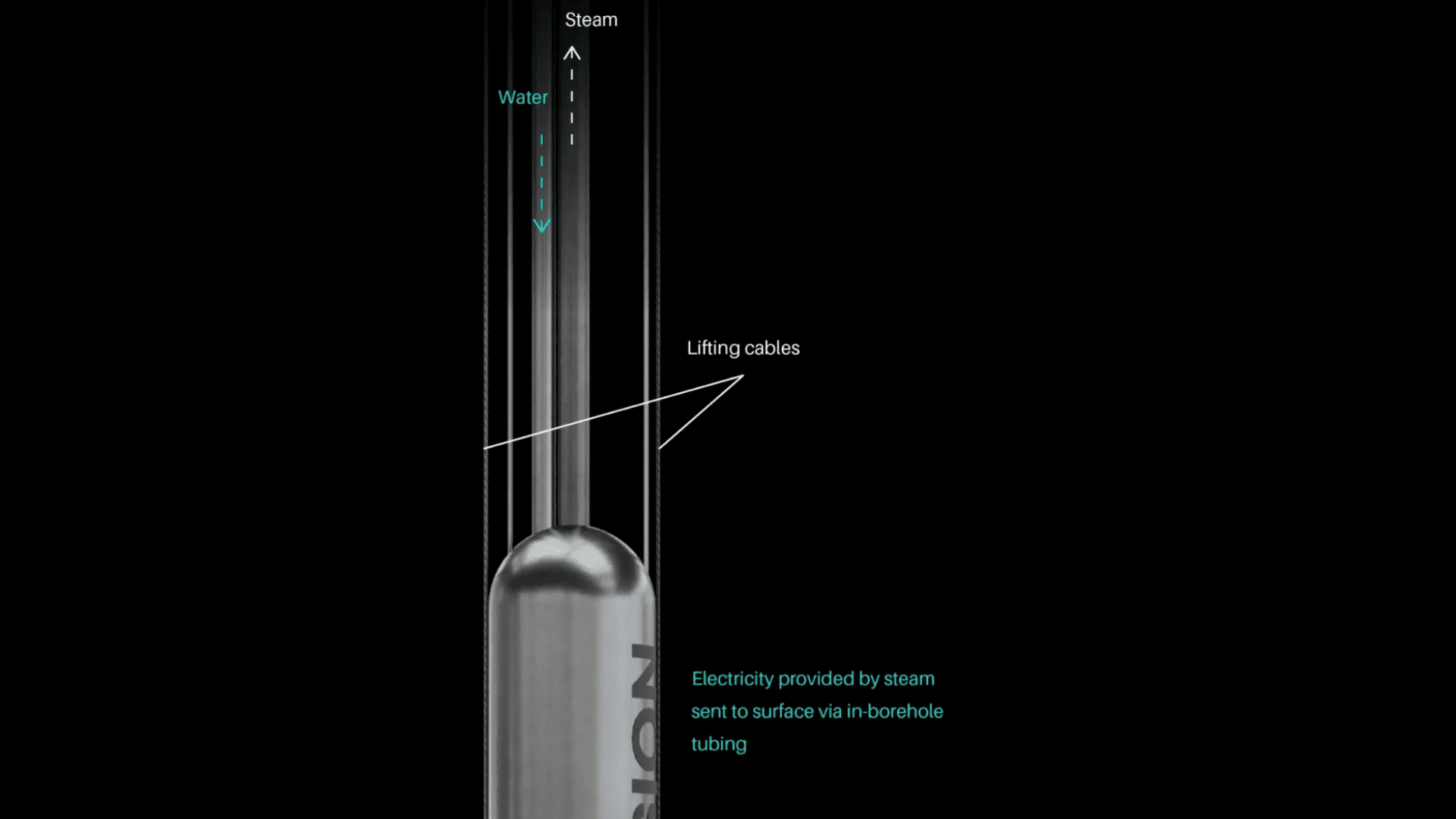
Nuclear fusion is the “holy grail” of clean energy because it is considered almost limitless. This has been the case for decades. However, scientists and engineers have long considered fusion to be just out of reach. As we move into 2026, the outlook on nuclear fusion is shifting from a lab experiment to a clean reality. We are moving away from theoretical physics and into massive engineering milestones.
Additionally, nuclear fission is becoming more accessible as the demand for clean energy continues to skyrocket globally.
Shifting Nuclear Fusion From Labs to Reality
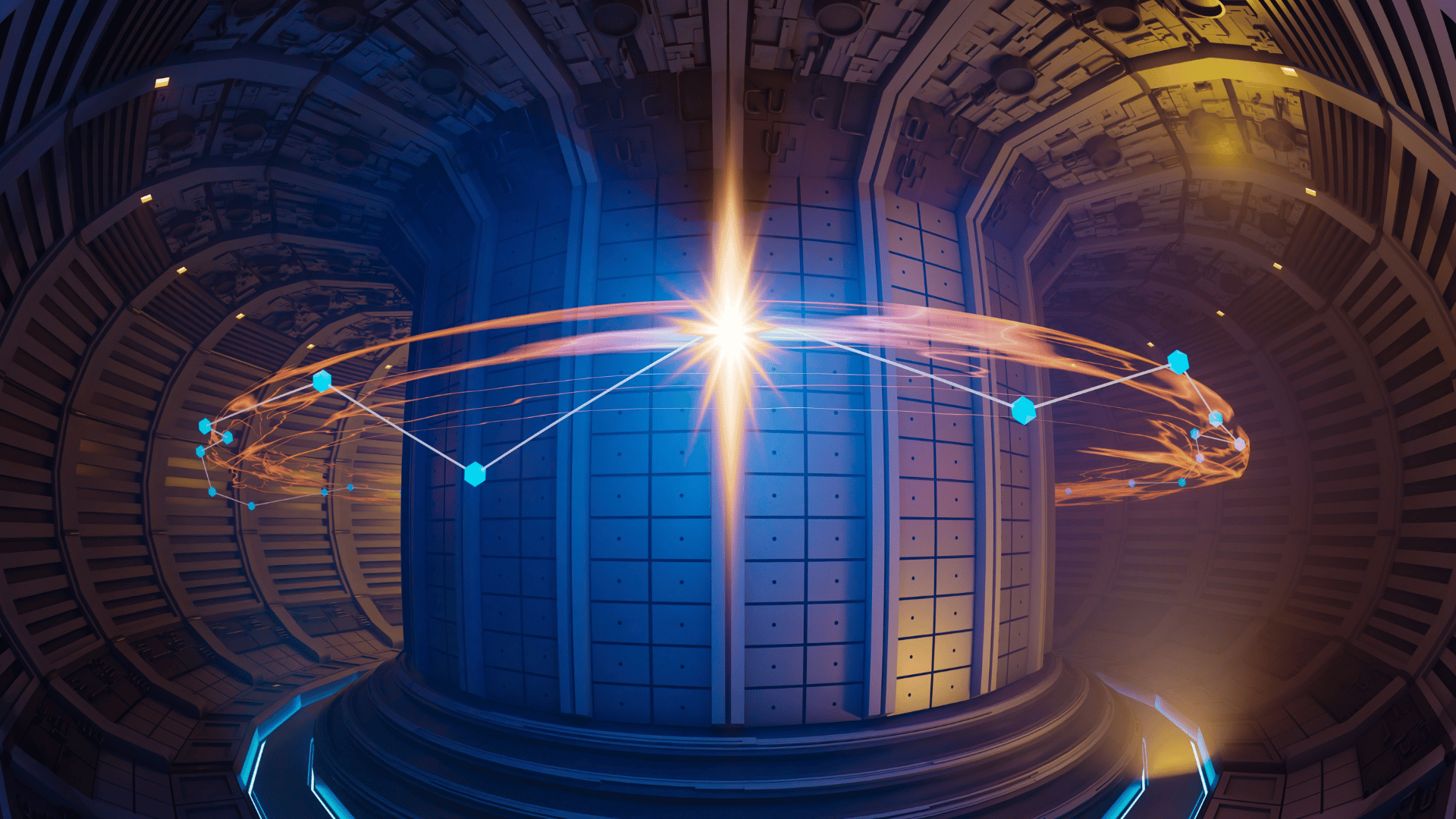

The biggest change in 2026 is the physical scale of progress. Fusion is transitioning from a “can we?” science experiment to a “how do we build it?” engineering feat. In Massachusetts, Commonwealth Fusion Systems is preparing to fire up its SPARC reactor. If it hits its goal of producing more power than it consumes, it will be a historic moment for clean energy comparable to the first flight.
Meanwhile, private companies like Helion Energy are pushing aggressive timelines with their Polaris machine. They aim to prove that fusion can be compact and commercially viable. Even on the international stage, South Korea’s “Artificial Sun” (KSTAR) is pushing the limits of physics by aiming to hold record-breaking temperatures for long enough to prove that fusion can be a steady, reliable backbone for the power grid.
Small Modular Reactors Make Nuclear More Achievable


While fusion is the North Star, traditional fission is having a major renaissance thanks to a tech-driven approach. The primary driver is the massive energy demand of artificial intelligence. Tech giants like Amazon and Microsoft are turning to nuclear power to keep their data centers running continuously.
The star of this movement is the Small Modular Reactor, often referred to as an SMR. In the 20th century, giant nuclear plants were the popular choice for producing clean energy. However, SMRs are designed to be built in sections in a factory and then shipped to where they are needed. This makes them smaller, safer, and much more flexible for a modern world that needs power quickly.
The Breakthroughs Behind the Scenes
Several technical advancements are making this nuclear push possible. New high-temperature magnets allow reactors to be ten times smaller than older designs. As a result, it drastically cuts costs and construction time. Scientists are also testing “fuel breeding” technology, where reactors essentially create their own fuel while operating.
Additionally, governments are beginning to streamline the process, which is considered one of the most important steps to scaling nuclear energy. Creating rules specifically for fusion that are separate from older nuclear regulations allows private companies to pave a clear path towards commercial nuclear energy.
As we approach 2026, clean and near-limitless energy feels closer than ever because of the technology, scientists, and engineers who work behind the scenes.